
AFLAPIN is a nutritional supplement used to reduce symptoms of osteoarthritis, such as joint discomfort and pain. It works by suppressing the enzyme 5-lipoxygenase, which is responsible for joint pain, swelling, and stiffness, and also protects cartilage. Overall, it helps improve physical function and mobility
Aflapin (50 mg): Aflapin is used in the treatment of osteoarthritis. It works by suppressing an enzyme called 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX), which is responsible for joint pain, swelling, and stiffness. Additionally, it protects the cartilage, the soft tissue that cushions the joints, and helps improve overall physical function and mobility1 .
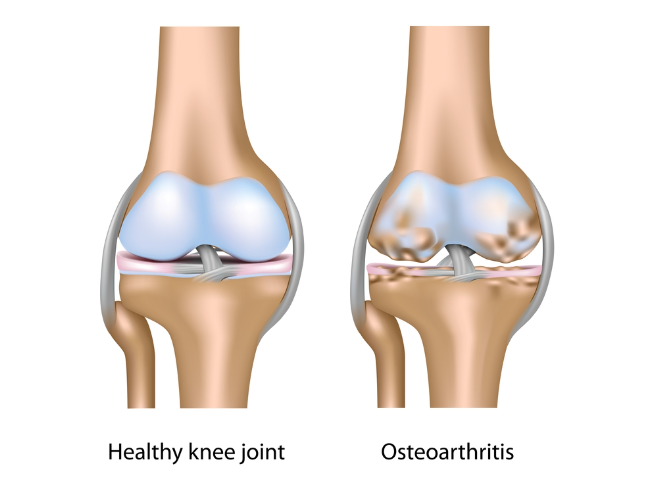
About AFLAPINAFLAPIN AFLAPIN belongs to the class of medications called nutritional supplements. It is primarily used to reduce the symptoms of Osteoarthritis such as joint discomfort and pain. It also improves flexibility and mobility. Osteoarthritis is a painful, degenerative, and inflammatory disease that affects synovial joints and eventually leads to loss of mobility.
Aflapin effectively reduces joint pain and inflammation when taken as a dietary mineral supplement. It reduces joint pain & stiffness by inhibiting the enzymes (5-lipoxygenase) that are responsible for joint pain, swelling and stiffness. It also improves flexibility, physical performance, as well as joint movement.
Take AFLAPIN as recommended. This medicine is
generally safe to use. In some cases, it may
cause nausea, diarrhoea, and heartburn. Most
of these side effects do not require medical
attention and resolve gradually over time. If
any of the side effects persist or worsen,
please consult a doctor.
Do not use AFLAPIN without doctor advice if
you had a skin reaction or irritation to any
medicine. Consult your doctor before using
AFLAPINif you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Keep your doctor informed about your health
condition and all the medicines you take to
rule out any side effects. It is unknown
whether it is safe to consume alcohol with
AFLAPIN. However, it is advisable not to take
or limit alcohol as a precautionary measure.
Osteoarthritis (joint pain and stiffness)
Aflapin (selective and potent 5-LOX
inhibitor).It relieves joint discomfort and
pain when taken as a dietary mineral
supplement. It works by blocking the enzymes
such as 5-lipoxygenase that cause
inflammation, thereby reducing joint
discomfort and stiffness. It also boosts
flexibility and physical performance.
Directions for Use
Swallow AFLAPIN as a whole with water; do not
crush or chew it.
Storage
Store in a cool and dry place away from
sunlight
Side Effects of AFLAPIN
Nausea
Diarrhoea
Heartburn
Aflapin , glucosamine, and chondroitin are all
popular supplements for managing knee pain,
particularly in osteoarthritis.
Here’s a comparison of their benefits and
effectiveness:
Source: Derived from Boswellia serrata (Indian
frankincense).
Mechanism: Inhibits inflammatory pathways,
reducing inflammation and pain.
Effectiveness: Clinical studies have shown
significant pain reduction and improved
physical function in as little as five days12 .
Safety: Generally well-tolerated with few
reported side effects3.
Glucosamine and Chondroitin
Source: Naturally occurring compounds in
cartilage; supplements are often derived from
animal cartilage or made synthetically.
Mechanism: Glucosamine aids in cartilage
formation, while chondroitin helps retain
water in cartilage and blocks enzymes that
break it down4 .
Effectiveness: Research is mixed. Some
studies show modest pain relief and improved
joint mobility, while others find little to no
benefit compared to placebo45 . The
combination of glucosamine and chondroitin has
shown some effectiveness in reducing knee
osteoarthritis pain and swelling4 .
Safety: Generally considered safe, but some
users report side effects like heartburn,
abdominal pain, and allergic reactions,
especially if allergic to shellfish5 .
Speed of Relief: Aflapin tends to show quicker results, often within a week, whereas glucosamine and chondroitin may take longer to show benefits.
Consistency of Results: Aflapin has more consistent positive outcomes in clinical trials, while glucosamine and chondroitin have mixed results .
Safety Profile: Both are generally safe, but Aflapin has fewer reported side effects . If you’re considering these supplements, it’s best to discuss with your healthcare provider to determine which might be most suitable for your specific condition and to avoid any potential interactions with other medications.
Drug InteractionsDrug-DrugInteractions: No interactions found / established.
Drug-Food Interactions: No interactions found / established.
Drug-Disease Interactions: No interactions found /established.
ALCOHOL CAUTION It is unknown whether it is safe to consume alcohol with AFLAPIN. However, it is advisable not to take or limit alcohol as a precautionary measure.
PREGNANCY CONSULT YOUR DOCTO Not enough scientific data is available for AFLAPIN. Hence it is advised to consult your doctor if you are pregnant or planning for pregnancy before taking AFLAPIN.
BREAST FEEDING CONSULT YOUR DOCTOR Not enough scientific data is available for AFLAPIN. Hence it is advised to consult your doctor if you are breastfeeding.
DRIVING CAUTION It is not known if AFLAPIN alters your ability to drive. Drive or operate machinery only if you are alert.
LIVER CONSULT YOUR DOCTOR Not enough scientific data is available for AFLAPIN. Hence it is advised to consult your doctor if you have liver problems.
KIDNEY CONSULT YOUR DOCTOR Not enough scientific data is available for AFLAPIN. Hence it is advised to consult your doctor if you have kidney problems.
CHILDREN CONSULT YOUR DOCTOR Not enough scientific data is available for AFLAPIN. Hence it is advised to consult your doctor if you have any concerns regarding the usage of AFLAPIN in children.
No
Weight is the essential connection between
diet and osteoarthritis. Obesity or being
overweight puts more strain on your joints.
Inflammation is also caused by excess fat,
which can exacerbate symptoms. Losing
weight helps decrease pain and
improve physical function and mobility.
An appropriate exercise can help you manage
your weight, keep your joints flexible,
strengthen muscles around your joints, and
offers more support.
Heat and cold treatments can help relieve
arthritis pain and inflammation.
A diet rich in fresh fruits, vegetables, and
whole foods can help boost your immune
system and overall health.
Avoid a diet like a diet rich in red meat,
processed foods, saturated fat, and added
sugar and salt might aggravate
inflammation, which is a characteristic of
arthritis.
Limit alcohol and caffeine intake and quit
smoking.
Disease/Condition Glossary
Osteoarthritis: Osteoarthritis is a painful, degenerative, and inflammatory disease that affects synovial joints and eventually causes loss of mobility.
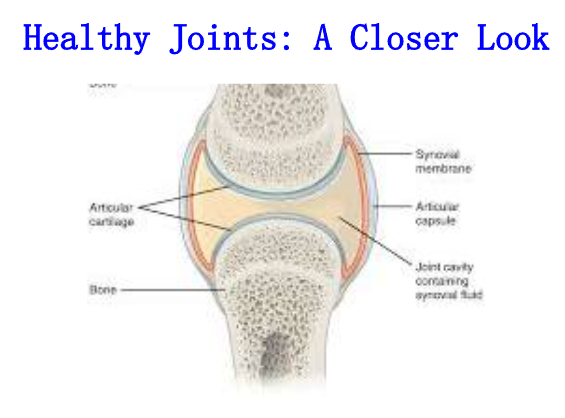
Joint stiffness: Joint stiffness/rigidity is the sensation of difficulty moving a joint or the apparent loss of range of motion.
Joint discomfort: Joint discomfort means pain or inflammation arising from any part of a joint.
Understanding Joint Mobility Joint mobility refers to the ability of your joints to move freely and easily. It's a crucial component of overall physical health and well-being. Healthy joints allow you to perform daily activities without pain or discomfort. When your joints are stiff or restricted, it can significantly impact your quality of life.
Factors
Affecting Joint Mobility
Several factors can influence joint mobility, including:
Age: As we get older, our joints naturally become less flexible.
Injuries: Accidents or overuse can lead to joint damage and reduced
mobility.
Medical conditions: Arthritis, gout, and other inflammatory diseases can
affect
joint function.
Lifestyle: Sedentary habits, poor posture, and excessive weight can
contribute
to joint stiffness.
Genetics: Some people may have a genetic predisposition to joint
problems.
Importance
of Maintaining Joint Mobility
Pain reduction: Good joint mobility can help alleviate pain and
discomfort
associated with joint
conditions.
Improved physical function: Flexible joints allow you to move more freely
and
efficiently,
enhancing your overall physical performance.
Enhanced quality of life: Maintaining joint mobility can significantly
improve
your quality of life
by enabling you to participate in activities you enjoy.
Reduced risk of falls: Good joint flexibility can help prevent falls,
especially
in older adults.
Tips for
Improving Joint Mobility
Regular exercise: Engage in activities that improve flexibility, such as
yoga,
tai chi, or swimming.
Strength training: Build strong muscles around your joints to provide
support
and stability.
Maintain a healthy weight: Excess weight can put extra strain on your
joints.
Proper nutrition: Consume a balanced diet rich in nutrients that support
joint
health, including
omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants.
Rest and recovery: Give your joints adequate time to rest and recover.
Avoid overuse: Don't push your joints beyond their limits.
Consider professional help: If you're experiencing persistent joint
pain or
limitations, consult a
healthcare professional for advice.
Remember, joint mobility is essential for a healthy and active life. By
incorporating these tips into your daily routine, you can improve your joint
health and enjoy a better quality of life.
Nutrition
for Joint Health
Omega-3 fatty acids: Found in fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and
sardines,
these healthy fats
can reduce inflammation and improve joint function.
Vitamin C: This antioxidant helps protect tissues from damage and may aid
in
collagen
production, a key component of joint cartilage.
Calcium and vitamin D: These nutrients are essential for bone health,
which
supports joint
stability.
Glucosamine and chondroitin: While research is ongoing, some studies
suggest
that these
supplements may help maintain joint cartilage.
Exercises
for Joint Health
Range of motion exercises: Gentle movements that help maintain joint
flexibility, such as arm
circles, leg swings, and neck rotations.
Low-impact exercises:Activities that put minimal stress on joints,
including swimming, cycling,
and walking.
Strength training: Building strong muscles can help support joints and
reduce stress.
Common Joint
Conditions
Osteoarthritis: A degenerative joint disease characterized by cartilage
breakdown.
Rheumatoid arthritis: An autoimmune disease that causes inflammation in
the
joints.
Gout: A type of arthritis caused by uric acid crystals forming in the
joints.
Bursitis: Inflammation of fluid-filled sacs (bursae) that cushion joints.
Preventing
Joint Problems
Maintain a healthy weight:
Excess weight can put extra strain on joints.
Protect joints from injury: Use proper form when exercising and wear
protective gear when
necessary.
Listen to your body: Pay attention to signs of joint pain or discomfort
and take steps to address
them.
Manage stress: Chronic stress can contribute to joint pain and
inflammation.
When to See a
Doctor
Persistent joint pain:
Persistent joint pain: If you experience joint pain that doesn't improve or
worsens over time.
Limited joint mobility: If you find it difficult to move your joints
normally.
Swelling or redness: If your joints are swollen or red.
Joint deformity: If your joints appear misshapen.
By understanding the factors that affect joint health and taking proactive steps to protect your joints, you can reduce your risk of joint problems and enjoy a more active and pain-free life.
Popular
Supplements for Joint Health
Boswellia:
This herb has been used traditionally to reduce inflammation and improve joint
mobility.
Glucosamine and Chondroitin:These compounds are naturally found in
cartilage and are often
used to support joint structure and function.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fatty fish like salmon and flaxseeds,
omega-3s can help reduce
inflammation and improve joint flexibility.
Vitamin C: This antioxidant plays a role in collagen production, a key
component of cartilage.
Calcium and Vitamin D: These nutrients are essential for bone health,
which supports joint
stability.
Curcumin: The active compound in turmeric, curcumin has
anti-inflammatory properties that
may help alleviate joint pain.
Hyaluronic Acid: A naturally occurring substance found in cartilage,
hyaluronic acid can help
lubricate joints and reduce pain.
Factors to
Consider
Dosage:
The appropriate dosage of supplements can vary depending on individual factors.
Quality:Ensure you're purchasing high-quality supplements from
reputable brands.
Interactions: Some supplements may interact with medications or other
supplements.
Individual needs:The effectiveness of supplements can vary from person to
person.
When to Consult a Doctor
Severe joint pain:
If you're experiencing significant joint pain that interferes with your daily
activities.
Underlying medical conditions:If you have a diagnosed joint condition or other health issues.
Allergic reactions: If you have a history of allergies or sensitivities to certain ingredients.
Lack of improvement:If supplements aren't providing the desired results after a reasonable
period.
Remember, while nutritional supplements can be a valuable tool for supporting joint health, they should be used as part of a comprehensive approach that includes a healthy diet, regular exercise, and appropriate medical care.
Disclaimer: While nutritional supplements can be beneficial for joint health, it's essential to consult with a healthcare professional before making significant changes to your diet or supplement regimen. Individual needs may vary.